June 20, 2025 • 17 min read
CSRD reporting requirements: What every compliance team must know

Kara Anderson
Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD) reporting is no longer optional for companies with ties to the European Union. The rules are firm, and the timeline is set. Whether your team sits in audit, compliance, or risk, the directive forces you out of old workflows. You now need facts, not forecasts. Data, not just intentions.
Controls, policies, and ESG reports all go public. Every number in your sustainability information can be scrutinized. Your board wants certainty. Your regulators want proof. Even your investors are watching for missteps.
The learning curve is steep. Most teams still sort through spreadsheets, emails, and half-finished checklists. But the law expects more detail: data on value chain impacts, materiality assessments, and evidence for every claim. You need information from teams scattered across countries and business units. That’s a lot to coordinate, especially when CSRD phases arrive fast.
Miss a requirement, and you risk fines or damaged credibility. Yet, companies using connected platforms, including solutions such as AuditBoard’s CSRD platform, gain a head start.
They centralize risk and ESG data, standardize controls, and support audit-readiness.
The cost of delay goes beyond penalties. Fall behind, and you’ll spend twice as long playing catch-up while competitors move ahead.
The CSRD isn’t just another regulation. It’s a test of how well your teams handle complexity. The leaders will be those who turn compliance into clear, accurate reporting before the deadlines hit.
What the CSRD is and why it matters
The CSRD changes how companies report on sustainability across Europe. The rules set higher standards, reaching thousands of businesses that never faced this level of scrutiny before.
The shift from NFRD to CSRD
The Non-Financial Reporting Directive (NFRD) covered a narrow set of public-interest entities. The CSRD expands the net. Large companies — listed or not — and even many non-EU entities with EU operations now have to comply. The expectations aren’t vague. Reports must cover detailed environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data vs. broad policies.
Teams that used to tick boxes now need structured evidence. Materiality assessments, value chain mapping, and data controls become routine. The change drives transparency and consistency, raising the stakes for audit, risk, and compliance functions.
Objectives and global implications
The EU isn’t raising the bar for its own sake. Regulators want ESG data that is consistent, comparable, and credible for investors, customers, and stakeholders. The goal: drive sustainable investments toward responsible businesses and drive accountability.
The CSRD’s reach extends beyond Europe. Non-EU companies with significant EU activity face the same reporting obligations, pushing global businesses to unify their reporting standards.
These objectives redraw the compliance map. Daily work shifts from compiling annual narratives to delivering year-round evidence that stands up to independent scrutiny. Companies that adapt early set themselves apart. They lower risk, win investor trust, and avoid last-minute chaos as deadlines approach.
Note: Key differences exist between CSRD and U.S. frameworks, like the climate disclosure rule from the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). These gaps affect who qualifies, what gets reported, and how data is verified, especially for global companies navigating both sets of standards.
Who needs to comply with the CSRD?
CSRD requirements don’t apply to everyone, but the net is wider than many expect. Both EU-based companies and certain non-EU companies with business in Europe now fall under the regulation.
EU-based companies and listed entities
Any large company established in the EU — listed and unlisted — comes under the CSRD if it meets at least two of the following criteria: more than 250 employees, €50 million in turnover, or €25 million in total assets on the balance sheet.
Listed small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) will also be included, with a longer phase-in. The aim is broad coverage: banks, insurers, and most public-interest entities are all in scope, no matter their sector.
Non-EU companies with EU operations
The CSRD doesn’t stop at Europe’s borders. If a non-EU company generates over €150 million in annual net turnover in the EU and has at least one EU subsidiary or branch, it must comply. These companies will need to report on group-level sustainability performance, even if their headquarters are on another continent.
Got stocks or bonds listed on an EU-regulated market? You're in too. Even if you're based halfway across the world, having securities traded in Europe pulls you into the CSRD's orbit.
For global firms, this means new disclosure requirements may hit sooner — and with more depth — than other ESG regimes.
Key compliance deadlines and phases
The CSRD enforces a strict timeline, and most teams underestimate how soon the requirements start. Reporting comes in waves, with large and listed companies leading the way. Don’t assume you have years. A phased approach means preparation must start now.
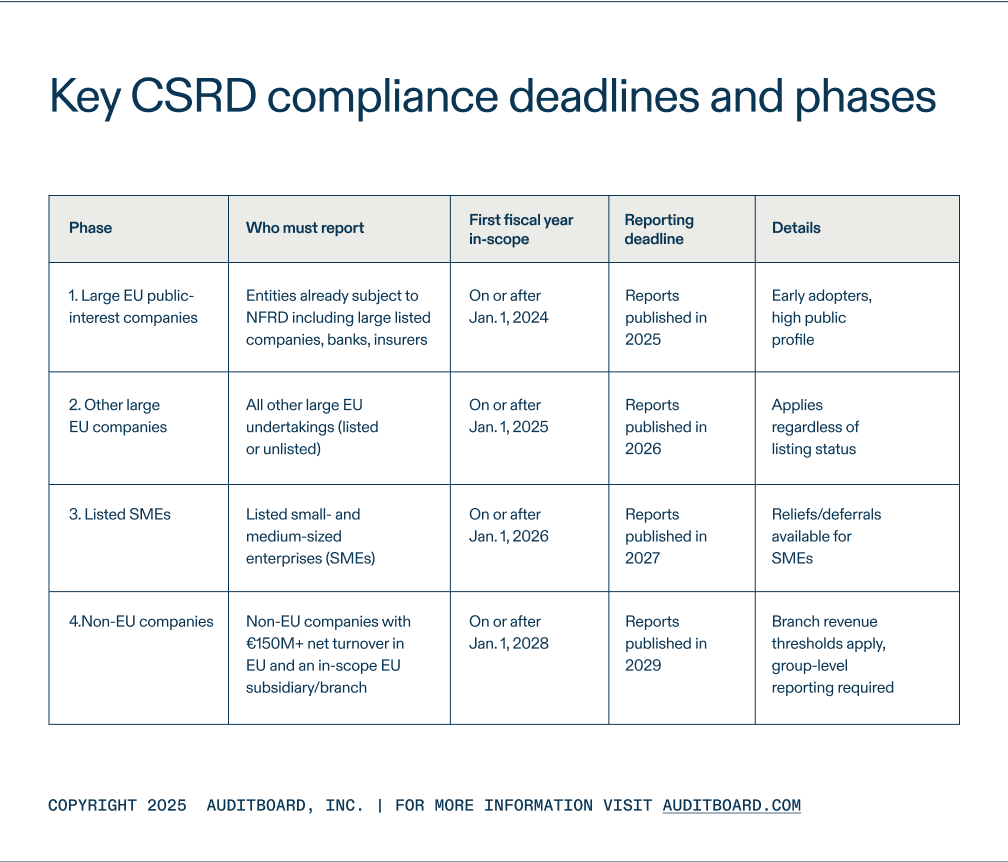
The first NESRS-based reports for non-EU parent companies are due in 2029. This phase ensures that companies with significant EU operations are held to the same standards as those headquartered inside the EU.
Missing a reporting phase isn’t a minor oversight. Organizations that wait until their deadline risk late compliance, rushed data gathering, and public errors. Early preparation is critical. Make sure to stay on top of ESG regulations, as ongoing changes continue to shape phase timing and readiness for compliance.
What the CSRD requires you to report
The CSRD isn’t checking for intent. The directive asks for facts backed by numbers, policies, and evidence that stands up to outside review. Every disclosure becomes part of your annual management report.
Vague statements or partial data won’t pass. Auditors and regulators will look for specifics, and stakeholders expect clear answers.
Double materiality and the ESRS framework
Every company must assess materiality from two angles: how sustainability issues affect your business (financial materiality) and how your business affects people and the environment. This “double materiality” goes further than previous standards.
You can’t just claim climate change matters; you need to show the financial risks tied to it, plus the broader social and ecological impacts of your operations, products, and value chain. Reporting must follow the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS), which set strict guidelines for what metrics and disclosures are required.
Materiality assessments shape your disclosures. They demand rigorous internal debate and clear documentation. The process should pull in voices from across business units, not just the sustainability team.
Auditability and third-party assurance requirements
The CSRD puts credibility front and center. Your sustainability data will need independent assurance, similar to a financial audit. Evidence collection can’t be left to last-minute hunts through inboxes and spreadsheets. Controls, processes, and calculations get tested.
If data is incomplete or unsupported, you face setbacks and scrutiny.
Third-party assurance means your reporting environment must hold up under real pressure. Teams need to build documentation, evidence trails, and review steps into everyday work. Companies that start these practices early will avoid last-minute chaos as auditors request backup for each disclosure.
CSRD reporting checklist: 5 practical steps
You can meet CSRD’s expectations — but only if everyone knows their role. Before you jump into the steps, set up a governance structure. Spell out who owns what, who keeps an eye on progress, and where people can go when they hit a roadblock. Oversight and accountability keep things moving and help you avoid last-minute scrambles as the rules evolve.
The rest comes down to having a process that works for real teams and real data. These five moves give you a practical way to build compliance into daily work, not just at year-end.
Step 1: Conduct a readiness assessment and gap analysis
Start with a blunt assessment of where you stand. Match your current ESG reporting, data collection, and controls against CSRD requirements. Identify missing disclosures, data gaps, and weak spots in your documentation. This step is about surfacing uncomfortable truths before the audit does.
Step 2: Align with reporting standards and map risks/controls
Don’t just rebrand your old ESG content. Map your policies, controls, and reporting processes to the ESRS framework. Identify overlaps between risk, compliance, and sustainability functions. This mapping lets you spot where evidence is reusable and where controls need realignment.
Step 3: Implement scalable data collection processes
Lack of control and traceability over spreadsheets creates problems for third-party assurance.
Build or buy data systems that track, store, and update ESG metrics across departments. Automate where possible, but require clear ownership for each data point. Consistency and traceability matter more than volume.
When it comes to emissions, you'll need extra care. These numbers aren't simple to track. You'll need data from multiple teams, and the math isn't straightforward. Give yourself plenty of time to get emissions right. They're often the most scrutinized part of your report.
If you need a single source for ESG data and controls, AuditBoard’s ESG management platform brings your reporting, documentation, and evidence together. One place for data. Fewer gaps. More confidence when audit season arrives.
Step 4: Engage stakeholders and train teams
The CSRD isn’t one team’s burden. Success depends on buy-in from HR, operations, facilities, and finance. Lead regular trainings. Bring stakeholders into scoping and review discussions, instead of just the year-end reporting cycle. People closest to the data need to understand compliance stakes.
Don't forget your supply chain partners. They hold data you'll need to report. Talk to them early and make sure they know what information you need and why it matters. A vendor who understands the stakes is more likely to give you accurate, timely data when crunch time comes.
Step 5: Plan for assurance and continuous improvement
Prepare for audits with advanced documentation and clear evidence trails. Schedule regular reviews of your process, learning from gaps and feedback after each reporting cycle.
Due diligence is everything. Double-check your numbers before they go into reports. Ask your team or outside partners directly: “Are we confident in this data?” A quick check now prevents headaches later when auditors start asking questions.
Continuous updates help you adjust to regulatory changes and keep your controls current. Staying aligned gets easier when you’ve got the risk basics down. If your team needs a refresher, practical risk management guidance makes adapting your process much more straightforward as things change.
Common CSRD compliance challenges and how to solve them
Most teams don’t miss compliance because of a lack of effort; they hit bottlenecks that slow down data collection, collaboration, or adaptation. Here’s where the biggest pitfalls show up, plus ways to break through.
Fragmented data across ESG and risk functions
ESG data lives in one system. Risk and audit controls live somewhere else. Teams trade spreadsheets, but information gets lost or mismatched. Fix this by building a single source for all CSRD data. Use platforms that link ESG, risk, and compliance metrics, reducing duplication and data drift.
Siloed ownership of ESG and financial reporting
Finance, operations, and sustainability functions don’t always speak the same language. When teams work in isolation, gaps appear in reporting and reviews drag on. You need joint ownership. A working group representing all key functions. Assign clear roles for data quality, review, and sign-off at each stage.
Take a hard look at how green initiatives change your business model. Will customers pay more for sustainable products? Do new regulations add costs? These questions matter for every team, not just the sustainability folks. Make sure your salespeople, product teams, and finance all tell the same story.
Staying ahead of regulatory change
CSRD requirements will evolve. Rules, technical standards, and best practices change fast. Teams that take a static approach fall behind and scramble at the last minute.
Schedule regular reviews of frameworks and procedures. Use tools and advisors that track updates and push new requirements directly to your workflows.
Tackling these issues head-on turns the CSRD from a compliance headache into a source of business strength.
Turn CSRD compliance into a source of value
The CSRD demands more than a checkbox approach. It calls for accurate data, strong processes, and team alignment. The right moves now set you up for smooth audits, fewer surprises, and real visibility into your ESG performance.
Companies that centralize their data and clarify ownership move faster and avoid last-minute panic. If you stay proactive, your disclosures become an asset, not a liability. CSRD isn’t a passing trend; it’s a new standard for transparency and trust that mandates a higher level of accountability.
Be the team that meets the moment, not the one playing catch-up.
Prepare for the CSRD with a connected platform that unifies risk, ESG, and compliance reporting — powered by AuditBoard.
About the authors

Kara is an SEO copywriter at Greenly, focusing on the UK market. She studied her bachelors of law at the University of Glasgow and her masters in international law at the University of Aberdeen, before looking for a more creative career path in advertising and freelance copywriting. Read more from Kara on the Greenly Blog.
You may also like to read


GDPR compliance requirements guide: What GRC managers need to know

How Cielo became the first RPO to achieve ISO 42001 compliance in just 3.5 months

8 best compliance automation tools

GDPR compliance requirements guide: What GRC managers need to know

How Cielo became the first RPO to achieve ISO 42001 compliance in just 3.5 months
Discover why industry leaders choose AuditBoard
SCHEDULE A DEMO



